Papillomas on the labia are a rather delicate problem that causes self-loathing and reduced quality of sexual life. They are difficult to hide, they can cause discomfort during sexual intercourse, so papillomas should be removed. In addition, in some cases, genital enlargement in women can be a dangerous risk of developing cancer.
Causes of papillomas
Papillomas on the labia or genital warts are the result of human papillomavirus infection. In total, there are more than 100 strains of this virus, which differ in the type of neoplasms and the degree of risk of developing oncology.
The virus enters the body mainly through sexual contact against the background of impaired immunity. At the same time, a man who has infected a woman may not have visible signs of the virus, since papillomas do not always appear on the skin in men.
Decreased immunity occurs against the background of recently transmitted infectious diseases, vitamin deficiencies or chronic stress. Papillomas on the labia can be caused by a decrease in local immunity, resulting in various inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genitals, including thrush and bacterial vaginosis. At the same time, for infection, it is enough to use other people's personal hygiene products, so that after a certain period of time, non-aesthetic formations appear on the labia.
Thus, despite the fact that the virus is transmitted from one person to another, the reasons for the appearance of papillomas on the labia in women are:
- Decreased immunity after ARVI, pneumonia, influenza or tonsillitis;
- Vaginal infections;
- Lack of personal hygiene;
- Stress;
- Unbalanced diet;
- The presence of a chronic focus of infection in the body;
- Obscene sex.
All of these factors lead to impaired immunity, both in general and locally. As a result, the body becomes susceptible to various negative influences and is unable to withstand human papillomavirus.
Often, the virus is not detected, is limited by human immunity. This is true only if the person is completely healthy. Then the virus can be asymptomatic in the body for a long time. Papillomas will develop on the background of impaired immunity. If this does not happen in the coming years, the body can cope with the virus independently, however, self-medication usually takes at least 18 months.
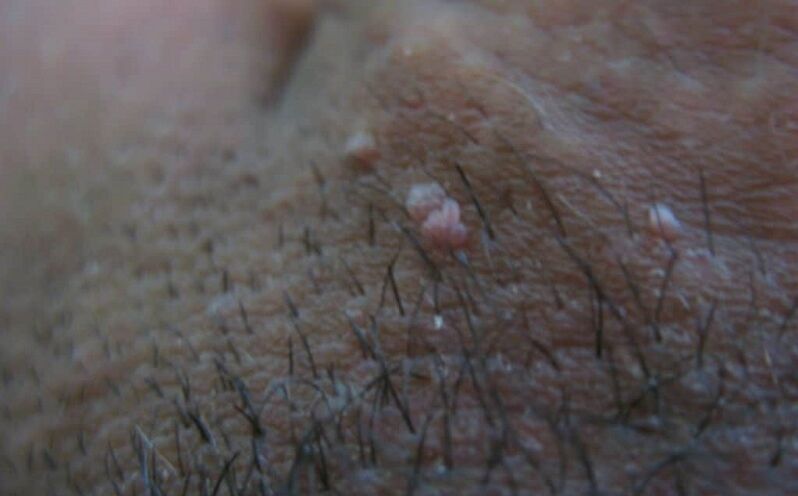
What do papillomas on the genitals look like?
How a woman's labia are detected depends on several factors:
- Virus type;
- Concentration of the virus in the body;
- Localization of growth.
The formation of papillomas on the labia minora is caused by the influence of oncogenic or conditionally oncogenic strains of the virus (types 16, 18, 31, 32, 45 and others). It is easy to understand what such papillomas look like on the labia, knowing what a condyloma is. These are small papillomas with yellowish edges that rise above the surface of the mucous membrane. They usually do not differ in color, or are slightly lighter than the mucous membranes. Manifestations of the papilloma virus on the labia, which provoke the development of genital warts, can spread to a woman’s perineum, vulva, and vagina.
Condyloma always arises only on the mucous membranes. In women, papillomas do not appear on the inner labia, they arise only in areas of thin epidermis.
Papillomas are small balls on the leg that rise above the skin. They have smooth borders of straight shape, may be slightly lighter or darker than the rest of the skin. When pressed, the papillomas do not hurt the labia, a uniform structure of growth is felt under the fingers. This type of neoplasm occurs in the folds of the uterus and on the large labia.
Almost any known method is used to remove papillomas on the labia, as the risks of epidermal burns or deep damage are minimal. Treatment of papillomas on the labia minora is carried out in a comprehensive manner, as such formations are potentially dangerous.
Warts can form in the following areas:
- Small labia;
- Vulva;
- Vagina;
- Cervix;
- Anal opening;
- Creut;
- Urethra
A photo of a papilloma on the labia is no different from images taken on other parts of the body, and papillomas or warts on the vagina and vagina are hardly noticeable.
The development of papilloma on the labia during pregnancy is associated with impaired immunity. In this case, timely treatment of HPV outcomes plays an important role, otherwise there is a risk of infection of the baby through the birth canal.
Why are papillomas dangerous?
In women, sexual contact and human papillomavirus are directly related. First, when in contact with the affected mucosa, there is a risk of transmitting the virus to a sexual partner. Second, friction during intercourse can damage papillomas and warts, accompanied by pain. There is a risk of becoming infected with papilloma when it becomes inflammatory and can begin to degenerate into cancer.
There are cases when a woman has a huge papilloma on a large labyrinth due to recurrent injuries. No woman is insured against such a risk. Large formations are very dangerous and must be removed first.
Pabilloma on the mucous membrane of the labia minora and vagina can lead to the development of cervical cancer. This is due to the activity of the papillomavirus, which is manifested by excessive division of epithelial cells in the small labia and other parts of the mucous membrane. In this case, the damage to the cervical cells develops in several stages. First, erosion develops on the labia of HPV, then it transforms into dysplasia, which is a precancerous condition. Lack of timely treatment of dysplasia leads to the development of cervical cancer.
It should be understood that any papilloma on the mucous membrane of the labia poses a potential threat. Papilloma itself can develop into cancer and not just provoke cervical oncology. Signs of a malignant papilloma include an increase in size, pain and itching, an increase in discharge with an unpleasant body odor, and blackening of the skin in the affected area. If you notice such symptoms, you should consult a doctor - oncologist, gynecologist or dermatovenerologist as soon as possible.
Treatment and removal of papillomas
How to treat papillomas on the labia depends on their number and size. It is advisable not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor who will tell you in detail what you need to do to remove and prevent papillomas on the labia.
Getting rid of papillomas on the labia should be consistent. First, the virus activity is suppressed, then the growth is removed and, if necessary, immunostimulatory therapy is administered. To accurately determine the sequence of treatment, a PCR analysis should be performed, which shows the degree and concentration of virus activity and also allows you to determine its severity.
If a woman is found to have a potentially dangerous strain of the virus, 16 or 18, complex therapy is needed. In this case, each removed papilloma is sent for histological analysis and a complete examination of the cervix is performed for changes in the epithelium.
How to remove papillomas on the labia depends on the exact location. Skin neoplasms are removed by any available means - from surgery to folk remedies. This is due to the fact that the skin of the big lip is thick enough, so complications rarely occur after removal. It is fair to say that formations on the large labia in most cases do not pose a health threat and do not provoke cancer.
Removal of genital warts on mucous membranes is performed using the method of laser exposure or radio waves. These two methods are considered the most gentle when they do not clog the vessels that increase growth, so the risk of bleeding is minimal. When removing neoplasms of the cervix or vagina, histological analysis is required to rule out the onset of an abnormal process.

You should consult your doctor about how to remove papillomas on the labia. If the analysis showed a high concentration of the virus in the body, there is a risk of recurrence of genital warts, therefore, complex therapy is carried out, including three stages.
- After determining the virus strain, the woman is prescribed antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy. This is necessary to prevent the virus and reduce the risk of papilloma recurrence.
- After drug therapy, which lasts an average of several weeks, the papillomas are removed in agreement with the chosen method and the doctor. Laser removal or radio wave method is recommended.
- Some time after removal of the growth, the analysis should be repeated. If the virus concentration is still high, a second course of drug therapy is prescribed.
Preparations used to treat papillomas are available in the form of tablets and ointments. Antiviral ointments with immunomodulatory properties are recommended for the treatment of papillomas on the skin. If lumps appear on the mucous membranes, it is indicated to take pills.
Typically, after papilloma removal and drug therapy, the body heals on its own after a few months or years. To prevent the re-formation of papillomas, a woman should follow the rules of hygiene, maintain her own immunity and avoid unprotected sex.














































































