Human papillomavirus (HPV, HPV - human papillomavirus) or papillomavirus is a group of infections that includes more than 100 types of virus, 80 of which are pathogenic to humans. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, 70% of the world's population is carriers of HPV. In most cases, the infection occurs after the onset of sexual activity and can be asymptomatic for a long time.
Causes of HPV infection
Symptoms of papillomavirus infection in women can include: various types of warts, flat and genital warts, cervical dysplasia. However, the most dangerous manifestation of the pathology is cervical cancer. There is also evidence linking the development of cancer of the anus, external genitalia, vagina with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV types 16, 18, 45, 56).
Transmission modes:
- Sexual contact.is the major route of transmission of human papillomavirus infection. The use of condoms during sexual intercourse significantly reduces the risk of infection with human papillomavirus, although it does not provide a reliable guarantee that the infection will not occur, since the viral particles are very small in size.
- Contact household path.Causes of infection are the use of joint intimate hygiene products: towels, soap, use of public toilet, bathroom.
- Natural childbirth.HPV can be transmitted to children who become infected when a baby passes through the birth canal of an infected woman.
The source of this infection is cells in the patient's skin and mucous membranes. In this case, the person may not be aware that he or she has become a carrier of the virus, since warts and papillomas can be microscopic in size and remain invisible on visual examination.
Predisposing factors that contribute to the development of viral infection:
- Start sexual activity at an early age;
- childless sex without the use of a condom;
- frequent abortions;
- presence of infectious diseases of the genitals; prolonged use of
- oral contraceptive methods;
- decreased body immune response;
- non-observance of personal hygiene rules;
- if your sexual partner has HPV;
- Impact of frequent stressful situations;
- Bad habits.
Through pores, cracks, microtraumas of the skin and mucous membranes, the virus reaches the basal layer of the epithelium, which ensures the normal growth and renewal of the skin and mucous membranes. The DNA of the basal layer cells (deoxyribonucleic acid) provides information about the healthy structure of the cells. The viral particle, inserted into the DNA, alters this information, resulting in the formation of affected cells, which in the process of growth and division cause the symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus infection in women
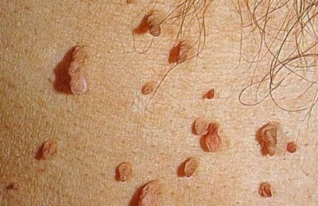
One of the possible manifestations of human papillomavirus infection is the appearance of genital warts and papillomas. These are specific formations that have a cauliflower, a bunch of grapes or a cock comb, pink - red or fleshy. Depending on the type and type of virus, they can infect human skin and mucous membranes.
Genital warts can form around or near the anus, especially if there is an anal connection.
Papilloma can occur on the fingers, fingers, hands, eyes, arms and scalp. They sometimes form on the soles of the feet and are characterized by characteristic pain when walking.
This type of disease rarely progresses to malignancy and cancer, although the tumors are surgically removed to prevent the disease from developing.
Consequences of HPV infection
Human papillomavirus in women can cause a significant increase in genital warts, papillomas, flat warts, which will cause discomfort, pain, and if they are damaged, bleeding of varying severity may occur.
Eighteenth and sixteenth types of HPV are the most dangerous because they cause cancer. Cervical cancer, which has been reliably linked to human papillomavirus infection, ranks second among various malignancies in women. Mortality from it reaches fifty percent.
Flat warts
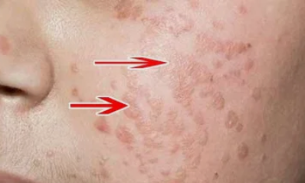
The disease is characterized by the formation of flat plaques that practically do not reach the level of the skin.
The most commonly damaged vaginal and cervical mucosa.
The cosmetic defect with them is much smaller than with genital warts.
This type of pathology has a risk of cancer recurrence.
Dysplasia of the cervical mucosa
Pathology is a change in the normal structure of cells in the cervical mucosa called atypia. This condition is considered precancerous in gynecology and requires observation and intensive treatment.
The disease is in most cases asymptomatic and is revealed during a routine examination by a gynecologist. Dysplasia of several degrees of severity is distinguished: mild, moderate, severe. The choice of treatment method depends on the severity.
Cervical cancer
This is the most dangerous manifestation of the disease. Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer pathology in women and is associated with HPV type 16, 18 infections.
The disease may continue without clinical signs or manifest with nonspecific symptoms: weakness, increased fatigue, weight loss, bleeding spots outside the menstrual cycle.
Methods of treating the disease
If there are signs of HPV infection, considering the risk of consequences, do not treat yourself.
In order to choose the optimal treatment tactics, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist, who will prescribe adequate therapy after a thorough examination and necessary tests.
The main directions ofTo date, no drugs have been invented that will cure HPV forever. The main goal of treatment is to reduce the concentration of the virus in the body to prevent further progression of the disease.
therapy:
Treatment of- manifestations (warts, papillomas, dysplasia);
- Antiviral therapy;
- Use of funds to increase immunity.
In the presence of papillomas, genital warts, warts, dysplasia areas, even small ones, their removal is recommended, as the presence of neoplasms increases the concentration of viral particles in a woman's body, which contributes to the further development of the pathology.
Surgical treatment
The methods of removing genital warts, papillomas, warts and dysplasia are as follows:
- surgical;
- cryotherapy;
- diathermy coagulation;
- laser coagulation;
- radiotherapy;
- Chemical attack.
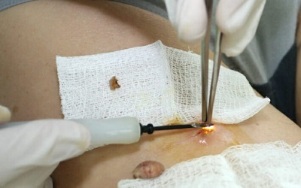
The surgical method involves removing the growths with a scalpel, is the cheapest method of treatment, however after that, a pronounced cosmetic defect remains and the healing period is considerably longer. There is also a risk of secondary infection. Therefore, this type of intervention is used in extreme cases.
During cryotherapy, liquid nitrogen is applied to the affected area, freezing the abnormal growth. After a few days the papilloma or condyloma disappears and a small wound forms under it, which heals in 10-14 days.
Diathermocoagulation is the application of high temperature to the affected skin areas. This procedure is quite painful and therefore requires anesthesia. The disadvantage of this method is the formation of rough scars at the site of abnormal growths.
Exposure to laser beams during laser coagulation on the affected area causes the neoplasms to dry out. In their place is formed a dry crust, which after a while disappears without leaving scars. This type of treatment is the most gentle, but its high cost is considered a minus.
Radiotherapy involves exposure to radiofrequency waves in the affected area. There is no risk of bleeding when using this type of treatment, pronounced scars do not form, but the disadvantage is the high cost.
The chemical method is used when there is a small formation. A special drug is applied to the affected area. After a few applications, a crust forms on the treated area, which disappears after a few days.
Drug use
Drug therapy for human papillomavirus infection involves the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Antiviral drugs;
- Immunostimulants.
A long course of antiviral therapy is prescribed to reduce the concentration of the virus in a woman's body and prevent it from multiplying further. Medications are used in the form of tablets and suppositories, the dose and duration of the course of treatment should be determined only by the attending physician.
Immunostimulants are prescribed after the analysis and detection of reduced levels of immunity, to strengthen the body, to accelerate the production of immune cells and to produce antibodies that are directed against the virus.
Treatment of HPV infection in pregnant women
The presence of human papillomavirus infection in a woman's body does not affect the reproductive system and is not a contraindication to pregnancy. If HPV is exacerbated during pregnancy, no therapy is given during this period, and treatment is prescribed after delivery.
However, a female doctor should be monitored throughout pregnancy. Gentle methods of therapy are prescribed when acute discomfort develops. In extreme cases, when there are contraindications to vaginal delivery due to HPV progression, a caesarean section is performed.
Get rid of HPV by folk remedies
At home you can use folk remedies such as herbal decorations and infusions - for the treatment of papillomatosis, ointments - to get rid of warts, papillomas and warts.
Ways to prepare decoctions and infusions for the treatment of human papillomavirus infection:
- Horse tail, nettle grass, rose petals, dandelion roots, plant leaves mixed in equal amounts. 3 st. Add 800 ml of water to the resulting mixture, boil for 10 minutes on low heat, then leave for 3 hours. Apply 1 cup 3 times a day 30 minutes before eating.
- Oregano herb, yarrow, immortality, St. John's wort, birch buds, nettle, calendula, rosemary, bush roots, chamomile flowers, strings, planting leaves, celandine, lime blossoms, bridge seeds mixed with sage. Pour 2 tbsp into a thermos. The resulting mixture, pour 500 ml of boiling water, leave for infusion overnight. Take 0. 5 cups 4 times a day.
- Valerian root, lemon balm, oregano, lime blossoms, hop cones, motherwort are mixed in equal amounts. Pour 1 tbsp into a thermos. The resulting mixture, pour 0. 5 liters of boiling water and leave for 3–5 hours. Apply 250 ml 2 times a day.
For treatment of local manifestations, contact:
- Celandine juice. The juice is made from fresh leaves or purchased at a pharmacy. Before using the product, the affected skin should be steamed and the healthy areas near the affected area should be treated with a greasy cream. Celandine should be gently applied to the affected skin. The procedure should be repeated twice a week until the abnormal formation disappears.
- Garlic. Grind the vegetables on a fine grater and mix with the skin cream until a viscous consistency is formed. Apply the resulting mixture on the formation sites for 2-3 hours for a month. After the procedure, wash your skin with soapy water.
- Young nuts. They should be crushed using a meat grinder, pour the resulting mixture into a 0. 5 liter glass jar so that it fills 2/3 full, pour the rest of the container with kerosene. Let stand for infusion for 20 days, then strain through cheesecloth. Infusion to treat affected skin 2 times a day.
After therapy and after recovering from the external manifestations of HPV, a woman needs to visit a gynecologist once every six months to monitor the disease and prevent further progression.














































































